INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
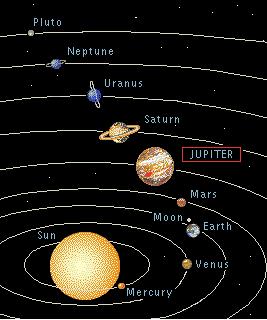
- Jupiter is the 5th planet
from the Sun, discovered by Galileo in 1610.
- Largest planet in Solar system.
- Named for the ruler of the gods in Roman mythology.
- First visit by Pioneer 10 in 1973; then Pioneer 11, Voyager 1 & 2, Ulysses.
- Spacecraft Galileo is orbiting around Jupiter.
- 1400 times volume of Earth but 318 times mass of Earth ==> Jupiter consists of gas.
- 11.9 Earth years to complete a revolution around the Sun.
- 9.9 hrs to spin on its axis ==> equatorial budge.

 COMPOSITION AND
STRUCTURE
COMPOSITION AND
STRUCTURE - Voyager 1 & 2 in 1979 gathered information about Jupiter.
- Atmosphere: H2 and He (like Sun), Dynamic weather system.
- Compare this to Earth's atmosphere.
- Gaseous material gets denser with depth.
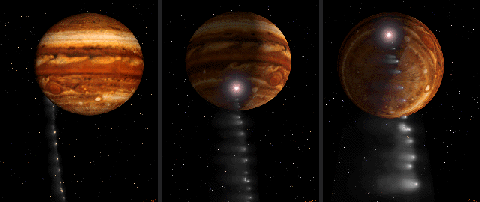
- Shoemaker-Levy 9 crashed into Jupiter in July 94 ==> more was learned about its atmosphere.
- Jupiter radiates twice as much energy as it receives from the Sun (due to slow gravitational compression).
- Periodic temperature flutuations in its upper atmosphere. ==> Reveal a pattern of changing winds like that of equatorial region of Earth's stratosphere.
-Temperature & pressure increase toward the interior ==> H2 liquifies ==> metallic, highly conducting state : Earthlike core.
 MAGNETIC
FIELD
MAGNETIC
FIELD- It's magnetosphere extends more than 650 million km.
- Generated deep inside the planet.
- At surface: 14 times stronger than Earth.
- Opposite polarity of Earth.
- Responsible for huge belts of trapped charged particles (electrons & ions) ==> Jovian magnetosphere.
 JUPITER'S SATELLITES
JUPITER'S SATELLITES- Jupiter has 16 known satellites which represent a miniature version of the solar system:
* 4 largest Galilean moons : Io, Europa (dense, rocky), Ganymede, Callisto (low density, composed of water ice).
* 12 small moons: Metis, Adrastea, Amalthea, Thebe, Leda, Himalia, Lysithea, Elara, Ananke, Carme, Pasiphae, Sinope.
 JUPITER'S RING
JUPITER'S RING
- Discovered by Voyager: a faint system of rings
- Uniform in its structure
- Composed of dust particles. (10 microns in diameter)
- Produced by the disintegration of small moonlets orbiting within the ring.
Mass (kg) ............................................................................................................. 1.900e+27
Mass (Earth = 1) ................................................................................................ 3.1794e+02
Equatorial radius (km) ............................................................................................... 71,492
Equatorial radius (Earth = 1) ............................................................................ 1.1209e+01
Mean density (gm/cm^3) ............................................................................................. 1.33
Mean distance from the Sun (km) ................................................................. 778,330,000
Mean distance from the Sun (Earth = 1) ............................................................... 5.2028
Rotational period (hours) .......................................................................................... 9.841
Orbital period (years) ............................................................................................ 11.8623
Mean orbital velocity (km/sec) ................................................................................ 13.07
Orbital eccentricity .................................................................................................. 0.0483
Tilt of axis .................................................................................................................... 3.13�
Orbital inclination ..................................................................................................... 1.308�
Equatorial surface gravity (m/sec^2) ...................................................................... 22.88
Equatorial escape velocity (km/sec) ...................................................................... 59.56
Visual geometric albedo ............................................................................................ 0.52
Magnitude (Vo) ......................................................................................................... -2.70
Mean cloud temperature ....................................................................................... -121�C
Atmospheric pressure (bars) ...................................................................................... 0.7
Atmospheric composition
Hydrogen .................................................................................................................... 90%
Helium ......................................................................................................................... 10%
Any comment & question send to:
Last updated: 05/21/96